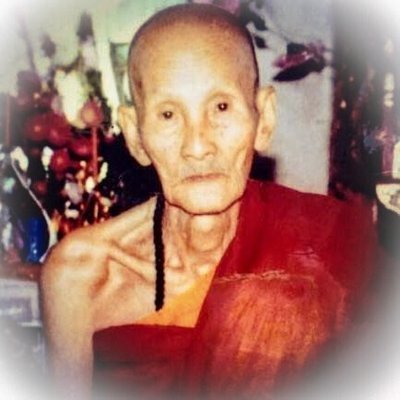
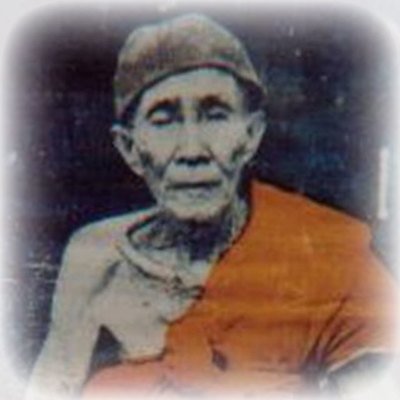
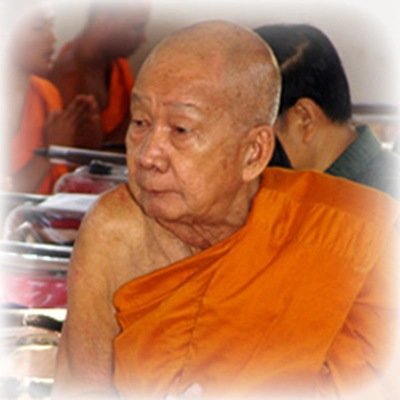
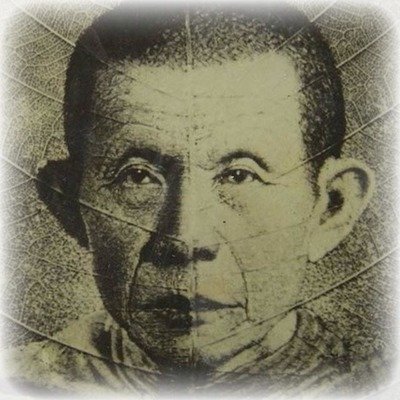
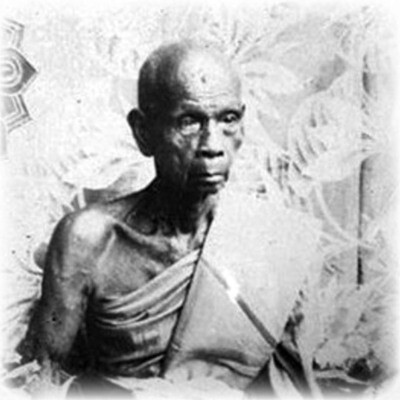
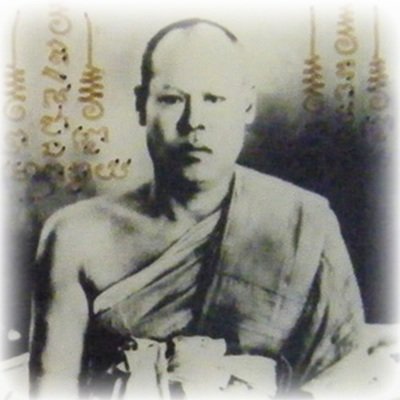
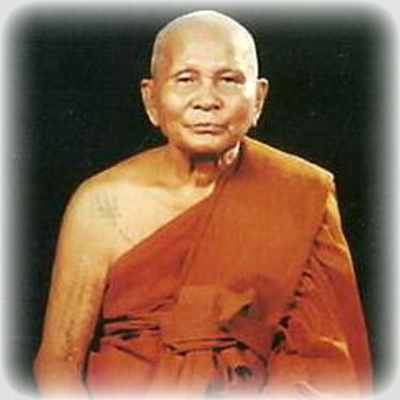
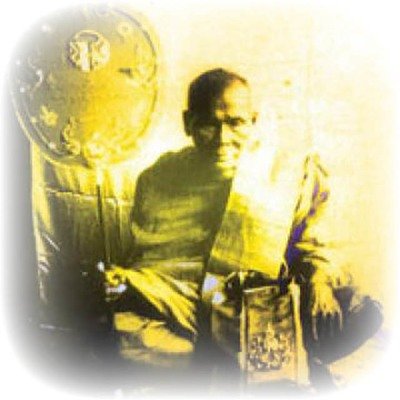
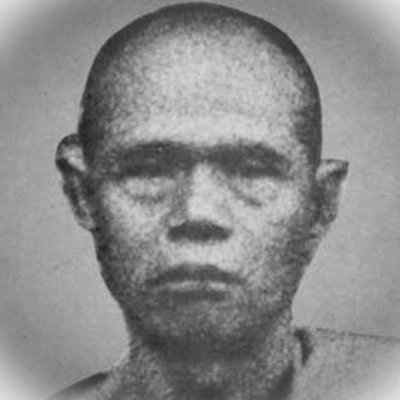
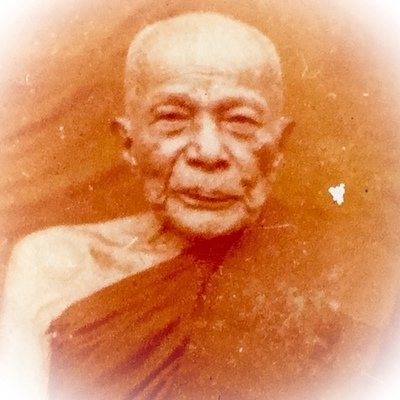
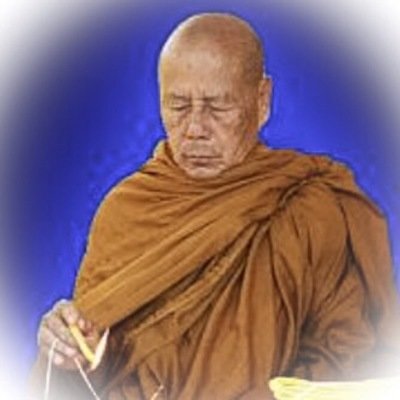
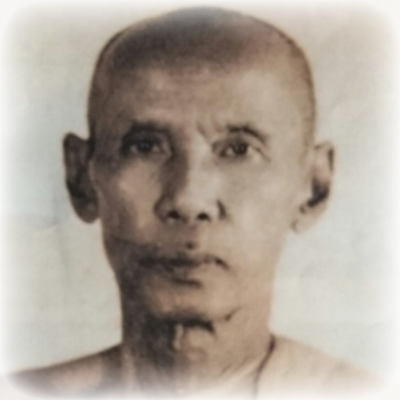
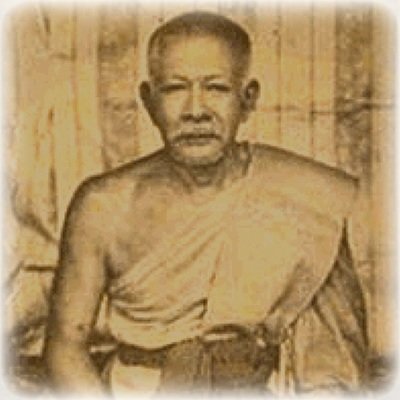
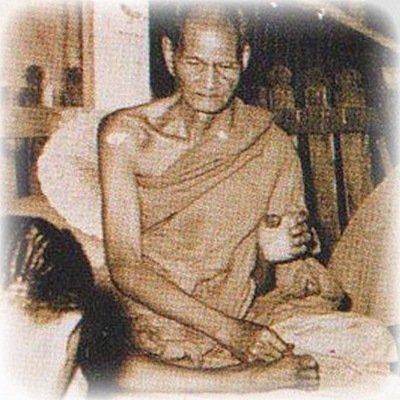
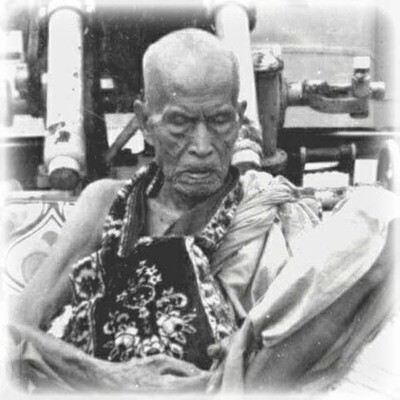
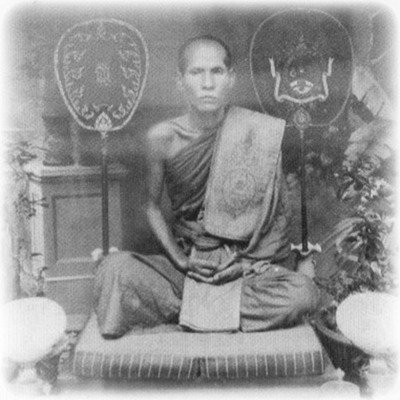
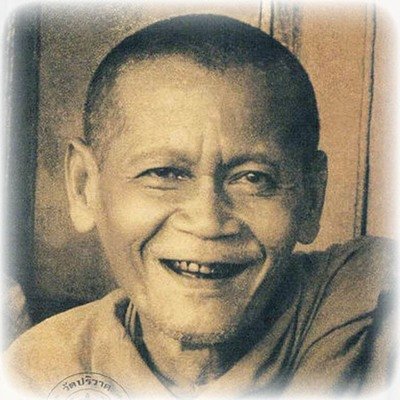
This list of Buddhist Guru Master monks will auto-update each time we add a new Master. Click each link in the list to view the amulets and read about each Guru Monk
- Ajarn Nong Wat Sai Khaw
- Luang Phu Yim Wat Nong Bua
- Luang Por An Wat Prayat
- Luang Por Daeng Wat Khao Bandai It
- Luang Por Glan Wat Prayat
- Luang Por Guay Chudtintaro Wat Kositaram
- Por Tan Nam Puttasaro Wat Don Sala
- Luang Phu Phueak Wat Ging Gaew
- Luang Phu Doo Wat Sakae
- Luang Por Chaeng Wat Bang Pang
- Luang Por Phaew – Wat Tanode Luang
- Luang Pu Seng Sopano Wat Kanlayanamit
- Luang Por Doon – Wat Buraparam
- Ajahn Chah Subhatto – Wat Nong Pha Pong
- Luang Phor Derm Phutthasaro of Wat Nong Pho
- Luang Por Ruesi Ling Dam – Life and Legacy
- Biography of Por Tan Klai
External Pages
- Luang Por Chuea Sugawanno (Wat Mai Bampen Bun)
- Luang Phu Nai – Wat Ban Jaeng (Ayuttaya)
- Luang Phu Rod (Wat Bang Nam Won)
- Luang Por Suang Apayo (Wat Chee Ba Khaw)
- Luang Por Nok (Wat Sangkasi)
- Luang Por Lae Tidtappo (Wat Khao Song)
- Luang Por Hyord (Wat Gaew Jaroen)
- Luang Por Pring – Wat Bang Bakork
Guru Masters
Ancient Thai Amulets from the all the Great Thai Buddhist Guru Master Monks of Yester-Year. Ancient Amulet is now Stocking Amulets from Currently over 144 Great Monks and rising
SIGN IN OR CREATE ACCOUNT

Pra Roop Muean Luang Por Thuat Nuea Krang LP Tong Sukh Wat Tanode Luang
Pra Roop Muean Luang Por Thuat Nuea Krang LP Tong Sukh Wat Tanode Luang
Free Shipping Worldwide & Offer of Free Casing
SKU 04731
$320